CRISPR Point Mutation Stable Cell Line
VectorBuilder는 관심 있는 게놈 타겟 사이트에 원하는 point mutation이 있는 안정적인 세포주를 제작할 수 있습니다. 이러한 point mutation은 HDR (homology-directed repair)을 위한 point mutation 주형을 운반하는 donor vector와 함께 타겟 사이트 특이적 gRNA/Cas9 RNP complex가 표적 세포에 도입되는 CRISPR 기반 방법을 사용하여 생성됩니다. VectorBuilder의 독점 기술을 통해 매우 효율적인 유전자 전달 및 HDR을 달성할 수 있고, homozygous mutant 획득에 대한 신속한 소요시간과 높은 성공률을 달성할 수 있습니다.
중점 사항
- Supreme point mutation efficiency: 독자적인 donor 디자인 및 유전자 전달 방법을 통해 세포는 최대 50%의 HDR 비율을 나타냅니다.
- Non-viral delivery approach: electroporation-based RNP 전달은 효율적이며 off-target effect가 낮습니다.
- Rapid turnaround:homozygous mutant 세포는 벡터 디자인부터 시작하여 빠르면 18주 만에 제작할 수 있습니다.
서비스 상세
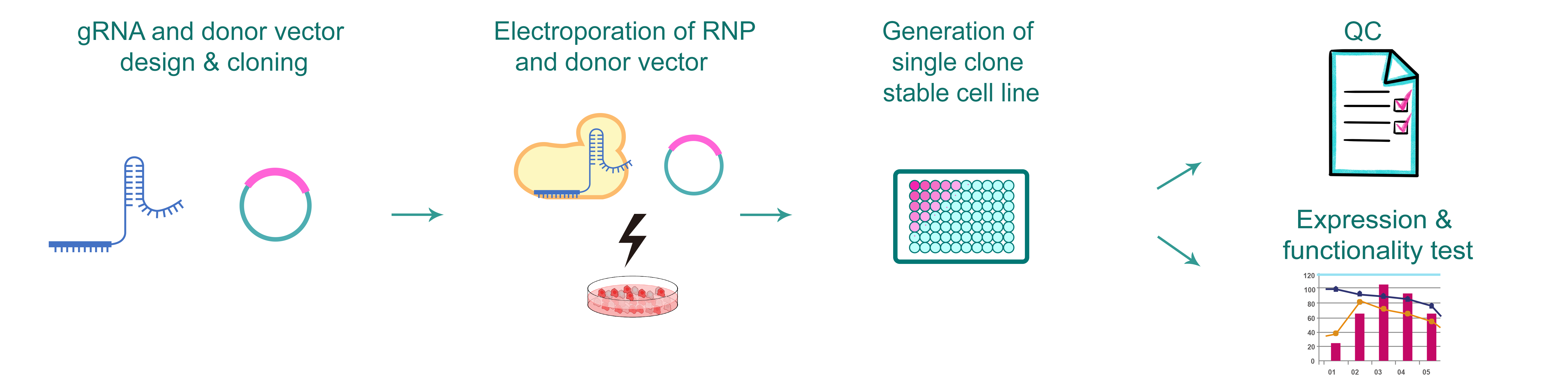
Figure 1.Typical workflow of CRISPR point mutation stable cell line production.
가격 및 소요시간
| Service Type | Deliverable | Price (USD) * | Turnaround |
|---|---|---|---|
| Point mutation | One homozygous single clone (>10 6cells/vial, 2 vials) | From $7,999 | 12-18 weeks |
* Additional charge will apply for extra single clones or vials.
QC assays
| Assay | Methods |
|---|---|
| Point mutation validation (default) | PCR, Sanger sequencing |
| Expression test (add-on) | RT-qPCR, WB, IF, FACS |
| Off-target analysis (add-on) | NGS, PCR, Sanger sequencing |
| Chromosome analysis (add-on) | Karyotyping |
| Sterility (default) | PCR for mycoplasma detection, bioburden test for sterility detection |
다운스트림 서비스
VectorBuilder는 proliferation, apoptosis, migration, viability, cytotoxicity 등에 대한 분석을 포함하여 제작된 세포주의 다양한 phenotype 평가 및 기능 검증을 수행할 수 있습니다.
사례 연구
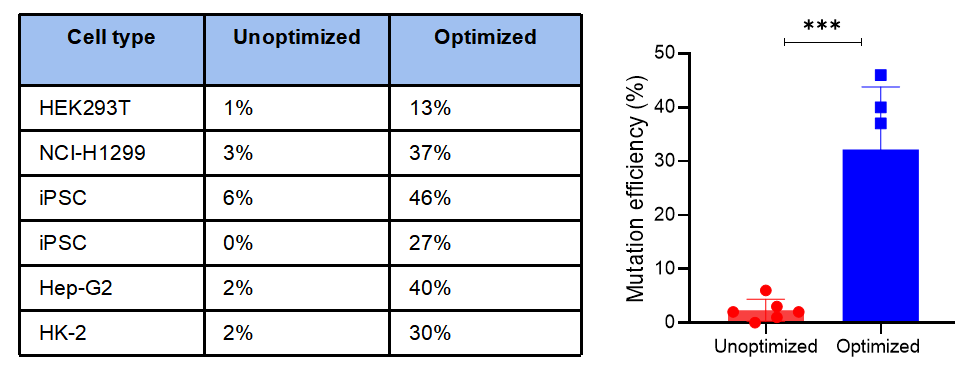
Figure 2. Point mutation rates in various cell types using our optimized mutagenesis strategy.
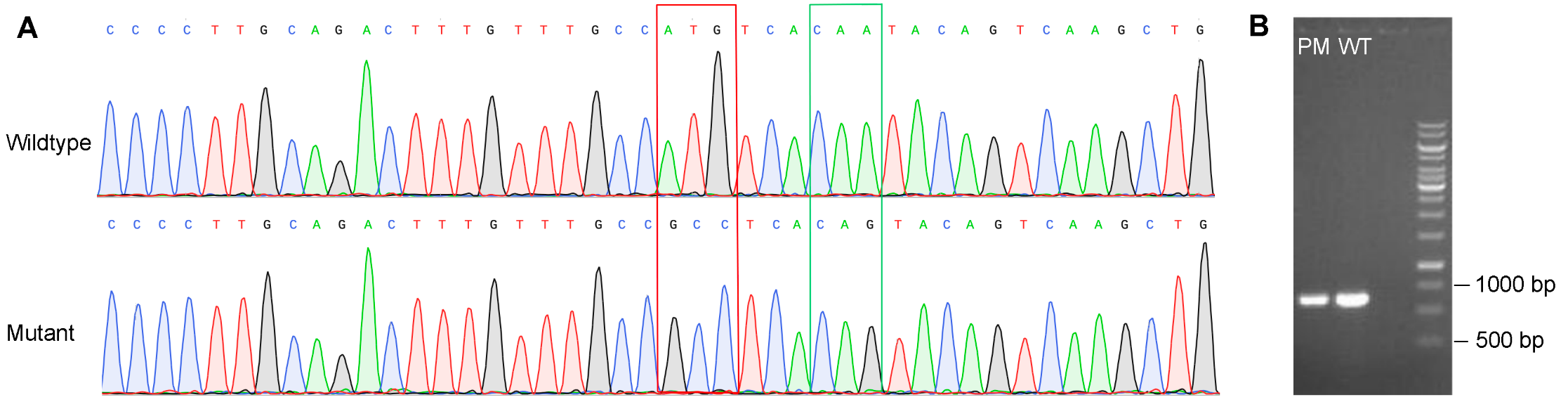
Figure 3.Validation of point mutations in THP-1 cells. (A) Point mutations in the GOI were verified by Sanger sequencing. The red square indicates nonsynonymous mutations and the green square indicates synonymous mutations. (B) Lengths of the PCR product of target site are the same for cells with point mutation (PM) and wildtype (WT) cells, indicating no structural mutation in PM cells.
주문 방법
자료
FAQ
For smaller fragments containing the mutation to be introduced, ssODN is a good option because of technical simplicity and its inability to integrate at random locations in the genome. However, for ssODN the template must be less than 200 bp. For larger fragments, dsDNA donors can be used. In either case, efficiency is increased when the cut-to-mutation distance is minimized to 10 base pairs for ssODN and 1 kb for dsDNA donors.
Although synonymous mutations produce the same amino acid sequence, they can affect codon biases, mRNA secondary structure and stability, and protein translation rates. Introducing synonymous mutations in cell lines allows the study of the effects of these post-transcriptional changes. Additionally, introducing a synonymous mutation that disrupts the target sequence for CRISPR components (e.g. PAM and nearby sequences) can suppress unwanted cleavage at off-target and previously CRISPR-Cas9 edited site.